Chicken remains the most widely consumed meat protein globally, driven by affordability, versatility, and efficient production systems. As global population growth, urbanization, and dietary shifts reshape protein demand, poultry continues to strengthen its position within the global meat industry. Production indicators between 2021 and 2025 show a steady upward trend despite macroeconomic disruptions, supply chain volatility, and global inflation pressures. These performance indicators highlight the resilience of the poultry sector and its strategic role in global food security.The data below, published by Statista, captures global chicken meat production from 2021 to 2025 in 1,000 metric tons (ready-to-cook equivalent)
. It excludes chicken paws and excludes production from Bahrain, Georgia, Iran, Jamaica, Moldova, and Venezuela. Total production increased by approximately
Total production increased by approximately 4.53 million metric tons over the 2021–2025 period, representing a cumulative growth of around 4.47% and an approximate CAGR of 1.1% annually.
The most significant year-to-year increase occurs between 2024 and 2025, signaling strong market recovery and rising demand.Year-to-Year Trend Interpretation
The production growth pattern across the five-year period reflects multiple stages of recovery and stabilization:2021 → 2022
Production rose from 101.35 million tons to 102.25 million tons, an increase reflecting stabilization after COVID-19 disruptions. During this phase, reopening economies and recovering logistics networks increased output capacity and consumption demand.2022 → 2023
Growth continued moderately, reaching 103.68 million tons. Demand strengthened due to improving restaurant and foodservice sectors, although inflation pressures and rising feed costs constrained more aggressive expansion.2023 → 2024
Production remained flat, increasing only slightly from 103.68 to 103.72 million tons. High feed prices—particularly corn and soybean meal—along with avian influenza challenges in several major producing regions, limited production expansion.2024 → 2025
The most notable growth occurred between 2024 and 2025, where production is estimated to jump to 105.88 million tons, an increase of 2.158 million tons. This suggests full market recovery, stronger purchasing power, and capacity expansion among leading producers.Key Growth Drivers (Supported by U.S. Consumption Analysis)
Multiple factors support the upward trajectory of global poultry production. Some drivers reflect global market behavior, while regional datasets, such as U.S. consumption, provide strong supporting evidence due to the market's size and influence.1. Consumer Preference for Affordable Protein
As food inflation pressure intensifies globally, consumers shift toward proteins that offer a more cost-efficient price-to-nutrition ratio. Chicken is consistently cheaper and more accessible than beef or pork in most markets, making it a preferred option for households and foodservice operators.Supporting this shift, per capita poultry consumption in the United States is projected to reach 118 pounds in 2025, according to IBISWorld, with an annualized growth rate of 1.0% between 2020 and 2025. The U.S. market is one of the largest poultry consumers in the world, making it a relevant indicator of broader demand dynamics. In 2022 alone, consumption rebounded by 2.1% to 114.3 pounds, driven by lower retail prices and inflation pressures encouraging consumers to prioritize poultry over other proteins.2. Foodservice & Restaurant Sector Recovery
The reopening of restaurants and tourism after pandemic restrictions has fueled additional demand for poultry products, especially processed and ready-to-eat chicken. Chicken is widely used in quick-service restaurants (QSR) globally due to its short cooking time, low cost, and broad cultural acceptance.3. Improved Supply Chain & Production Efficiency
As global logistics networks recovered, poultry production benefited from improved feed supply, processing throughput, and export shipping reliability. Investments in automation and vertical integration have also lowered operational costs for major producers.4. Competitive Position Against Other Meats
Beef and pork industries face more significant challenges related to:- Higher production costs
- Environmental impact concerns
- Disease risks such as African swine fever
- Intensive land and water requirements
In contrast, poultry offers:- Lower carbon footprint per kilogram of protein
- Shorter production cycles
- Higher feed conversion efficiency
These advantages strengthen poultry’s dominance as a practical protein solution for modern food systems.Challenges Facing the Poultry Industry
Despite consistent growth, several challenges continue to influence the sector:Rising Feed Prices
Feed accounts for 60–70% of poultry production costs. Price volatility in global corn and soybean markets increases financial pressures on producers, especially in price-sensitive regions.Disease Outbreaks
Avian influenza outbreaks have led to supply reductions and trade restrictions in several countries. The risk of rapid spread remains a central concern for producers and regulators.Environmental & Sustainability Expectations
Concerns about emissions, animal welfare, and land use are driving pressure for more sustainable production methods. Retailers and global brands are increasingly demanding traceability and lower-impact farming practices.Trade Policy & Geopolitical Tension
Tariffs, import restrictions, and political conflict continue to affect global poultry flows. Market access challenges influence both price stability and production planning.Implications for Food Industry & Global Trade
Growth in poultry production carries significant consequences for multiple industries:Impact on Food Prices
As poultry becomes more widely available, it helps stabilize protein prices globally, reducing inflation pressure for consumers and foodservice businesses.Supply Chain & Logistics Requirements
Cold chain logistics, processing technology, and export infrastructure are increasingly critical as global consumption expands.Opportunities for F&B Operators
Restaurants and packaged food manufacturers benefit from reliable pricing and broad consumer acceptance, enabling product diversification such as:- Ready-to-eat meals
- Frozen processed chicken
- Value-added flavor and health-focused products
Market Expansion for Halal Poultry
Growing Muslim population demographics—particularly in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa—are driving demand for halal-certified poultry. Exporting nations with halal-compliant processing stand to gain significant market advantage.Outlook for 2026 and Beyond
Current data trends indicate continued production growth through 2026 and beyond. Key factors supporting future expansion include:- Projected increase in global protein demand, especially in Asia and Africa
- Farm automation, genetic improvements, and smart feeding technologies
- Retail innovation in ready-to-cook and ready-to-eat poultry products
- Continued restaurant and fast-food expansion in emerging markets
However, sustainability pressure and feed price volatility may shape future investments and policy landscapes.Conclusion
Global chicken meat production has demonstrated robust growth from 2021 to 2025, increasing from 101.35 million tons to an estimated 105.88 million tons. This steady upward movement, despite inflation, supply chain disruptions, and disease challenges, reinforces poultry’s essential role in global food security and consumer nutrition.Growth drivers, including affordability, supply chain recovery, and consumer preferences may continue to support rising demand. Supporting U.S. consumption data further illustrates how poultry remains a resilient protein even during economic strain. Looking ahead, opportunities for expansion remain strong, particularly in value-added processing, halal certification, and technology-enabled productivity.For food industry stakeholders, investors, and policy leaders, understanding these production dynamics is critical for navigating pricing decisions, sourcing strategy, product planning, and long-term market positioning. 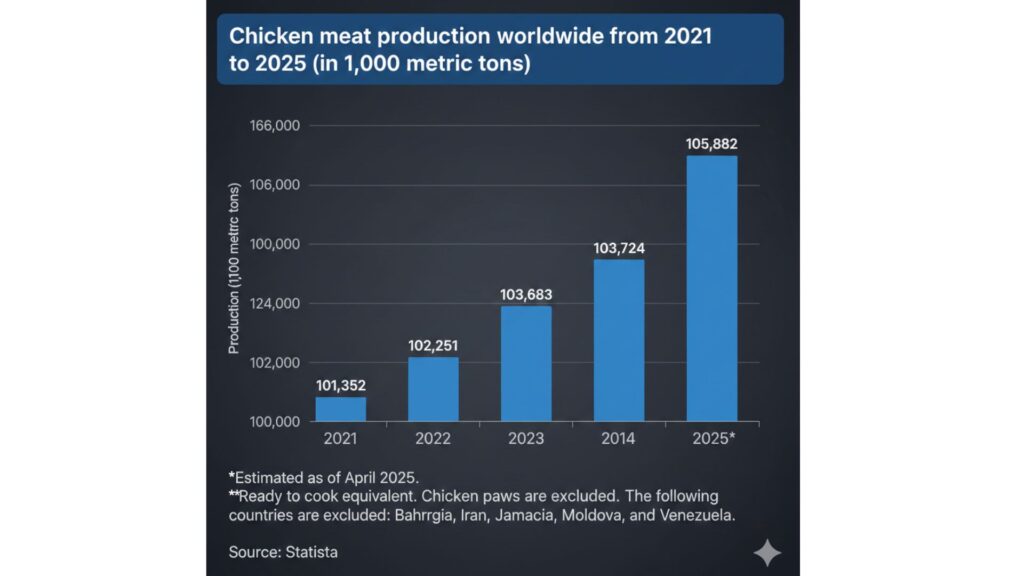 Total production increased by approximately 4.53 million metric tons over the 2021–2025 period, representing a cumulative growth of around 4.47% and an approximate CAGR of 1.1% annually.The most significant year-to-year increase occurs between 2024 and 2025, signaling strong market recovery and rising demand.
Total production increased by approximately 4.53 million metric tons over the 2021–2025 period, representing a cumulative growth of around 4.47% and an approximate CAGR of 1.1% annually.The most significant year-to-year increase occurs between 2024 and 2025, signaling strong market recovery and rising demand.
